Types of AI Tools Explained
Whether you’re looking to enhance lessons, support independent learning, or introduce new skills, understanding the types and features of AI tools is the first step.
Therefore this section helps educators explore the landscape of AI tools available for adult learners. It introduces key categories of tools, explains their functions and practical uses, and offers real-world examples to make teaching and learning more relevant.

UNDERSTANDING AI TOOL TYPES
Different Types of AI Tools
Artificial Intelligence has its roots in ancient philosophy, but modern AI began in the 1950s with pioneers like Alan Turing and John McCarthy. The 1956 Dartmouth Conference marked the official birth of AI as a field. In the 1970s–80s, AI faced setbacks known as the “AI winters” due to limited progress and high expectations. The resurgence began in the 2000s with advances in computing power, big data, and machine learning. Today, we live in the era of generative AI, with tools like ChatGPT and DALL·E becoming part of daily life. Understanding this history helps learners appreciate how far the field has come—and where it may go next.
Transversal Tools (General-purpose AI)
These tools are flexible and widely applicable across many contexts and subjects. Learners can use them for multiple purposes—from writing and research to organizing tasks.
Transversal tools are typically built using large language models (LLMs) or foundation models trained on massive datasets across many domains (e.g., books, websites, conversations). Tools like ChatGPT or Gemini are based on transformer architecture and use unsupervised machine learning on billions of text samples, followed by instruction tuning to better respond to human input.
Examples:
- ChatGPT / Gemini – Answering questions, summarizing texts, writing drafts
- Perplexity AI – Information search with cited sources
- Notion AI / Microsoft Copilot – Productivity support (writing, organizing, task lists)
Great for: Teaching foundational AI skills, digital literacy, and problem-solving.
Specific Tools (Task-focused AI)
These tools are designed for one main function and often serve a niche or practical use case. They help learners accomplish specific tasks more efficiently.
Specific AI tools are developed using narrow AI models designed and trained for one or a limited set of tasks—such as voice recognition, text-to-speech, or image generation. These models often rely on supervised machine learning, using labeled datasets relevant to their specific function, and are optimized for accuracy and performance within their domain.
Examples:
- Canva AI / Adobe Firefly – Graphic design and image generation
- Natural Reader – Text-to-speech for reading articles and books aloud
- TripIt AI / Roam Around – Travel itinerary planning
- Runway ML – Video editing and content generation
- Speechify / Bookshare – Accessibility and audio learning
Great for: Subject-specific tasks (e.g., media creation, language learning, accessibility).
AI BUILDING BLOCKS
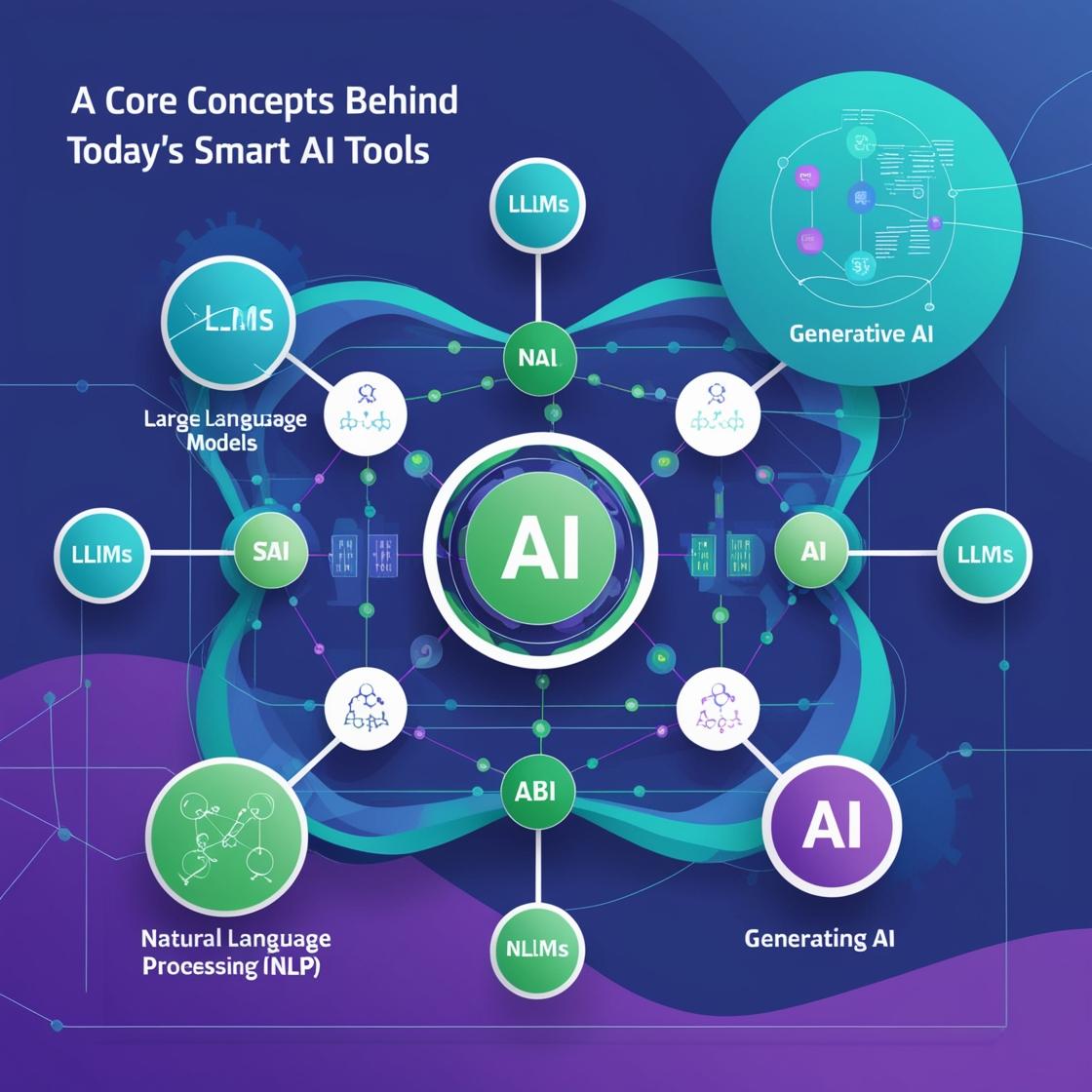
Core Concepts Behind Today’s Smart AI Tools
To use AI tools confidently, it helps to understand the powerful technologies that make them work. Three essential AI concepts—Large Language Models (LLMs), Natural Language Processing (NLP), and Generative AI represent key technologies enabling AI tools to understand, respond, and even create human-like language, images, and more.
-
Large Language Model (LLM)
A type of AI trained on massive amounts of text to understand and generate human-like language. - LLMs are the engine behind many AI tools—they provide the ability to respond with fluent, context-aware language.
- Example: ChatGPT, Gemini, Claude
-
Natural Language Processing (NLP)
The field of AI that focuses on how machines understand, interpret, and generate human language. - NLP is the method that allows machines to “read” or “listen” to human language and turn it into something an AI can work with.
- Used in: chatbots, translation apps, voice assistants
-
Generative AI
AI that can create new content—such as text, images, music, or video—rather than just analyzing data. - Generative AI is about creativity—it uses models like LLMs to produce entirely new content based on prompts or patterns.
- Examples: ChatGPT (text), DALL·E (images), Runway ML (video)

What AI can do
Common Features of AI Tools
AI tools come with a variety of features that help users accomplish tasks more efficiently, creatively, or accessibly. This section introduces the most common functions—such as generating text, finding information, creating visuals, or converting speech—and explains how each feature can be used in real-life learning and everyday situations.
Common Features of AI Tools, What They Do and Examples of Use
- Text Generation
- Writes essays, emails, content
- Examples: Drafting messages, creating stories
- Information Search
- Finds accurate data with explanations
- Examples: Researching health, travel, history
- Image Generation
- Creates pictures based on a prompt
- Examples: Creates pictures based on a prompt
- Speech-to-Text
- Transcribes spoken words into text
- Examples: Note-taking, accessibility
- Text-to-Speech
- Reads digital text aloud
- Examples: Listening to articles, books
- Translation
- Converts language in real time
- Examples: Multilingual communication
- Summarization
- Condenses long texts
- Examples: Understanding articles, reports
- Personalization
- Adapts suggestions to user behavior
- Examples: Recommending music, movies, products
Tips for Educators
- Start with transversal tools to build general AI familiarity.
- Use specific tools when introducing tasks like video editing or audio transcription.
- Encourage learners to try multiple tools and compare results.
- Emphasize free or freemium tools to ensure access for all learners.

